Wrist Arthritis (SLAC wrist)
SLAC wrist is a common type of wrist arthritis. SLAC stands for “Scapho-Lunate Advanced Collapse.” This occurs when the bones of the wrist abnormally wear down the cartilage surfaces, causing osteoarthritis. SLAC wrist can occur after injury to the ligaments that stabilize the wrist bones, most commonly the scapholunate ligament. Many patients who suffer from SLAC wrist experienced an injury that they thought was “just a sprain.” Other patients cannot remember a specific injury once SLAC wrist symptoms arise, since the injury may have occurred many years ago.

SLAC Wrist Symptoms
SLAC wrist typically develops as a result of long-term wear and tear or an untreated wrist injury, particularly involving the scapholunate ligament. The scapholunate ligament connects two important wrist bones, the scaphoid, and the lunate, and helps maintain the stability and proper alignment of the wrist joint. When this ligament is damaged or weakened, it can lead to SLAC wrist, which can cause various symptoms. Patients with SLAC wrist often notice limited range of motion, grip weakness, wrist pain, and swelling. It may be harder to use hand tools and lift heavy objects. Clicking and popping in the wrist may also occur.
Let’s take a closer look at the various symptoms that may present when a patient is suffering from SLAC wrist arthritis.
Pain
SLAC wrist is characterized by persistent pain in the wrist joint, which can significantly affect a person's quality of life. This pain can vary in intensity and type, and it typically results from degenerative changes and instability within the wrist joint.
Here's a more detailed explanation of the pain associated with SLAC wrist:
Chronic Nature
SLAC wrist pain is often chronic, meaning that it persists over an extended period of time. This chronic pain can be particularly frustrating for individuals as it may impact daily activities and overall well-being.
Dull and Achy Pain
Many people with SLAC wrist experience a constant, dull, and achy pain in the wrist joint. This type of pain can be likened to a persistent discomfort or a low-grade throbbing sensation. It may be present even during periods of rest or inactivity.
Sharp Pain
In addition to the dull and achy pain, individuals with SLAC wrist may also experience episodes of sharp, shooting pain. This sharp pain can be triggered by specific movements, activities, or positions that place stress on the compromised wrist joint.
Aggravation with Movement
SLAC wrist pain is often exacerbated by wrist movements. Activities such as bending the wrist, gripping objects, or lifting items can intensify the pain. As a result, individuals with SLAC wrist may find it challenging to perform tasks that require wrist mobility or strength.
Limitation of Activities
Due to the persistent pain and discomfort associated with the SLAC wrist, individuals may gradually limit or avoid activities that worsen their symptoms. This can lead to a decrease in functional capabilities and a reduced ability to participate in work, sports, and hobbies.
Impact on Quality of Life
SLAC wrist pain can have a profound impact on a person's overall quality of life. The constant presence of pain can lead to sleep disturbances, mood changes, and decreased productivity, affecting both physical and emotional well-being.
Swelling
Swelling around the wrist joint is common in SLAC wrist. This swelling can be noticeable and may contribute to discomfort and limited range of motion. Swelling is often a persistent symptom in SLAC wrist, and it may worsen as the condition progresses.
Limited Range of Motion
A limited range of motion is a significant consequence of SLAC wrist progression, impacting the functionality of the affected wrist joint. As this condition advances, individuals often experience a notable reduction in their wrist's range of motion, making it increasingly challenging to perform various everyday activities. This limitation manifests in several ways, primarily affecting the ability to flex and extend the wrist fully. The limited range of motion in SLAC wrist can have functional implications. It may affect one's ability to grip objects securely, causing difficulties in activities like lifting heavy objects and gripping.
Weakness
Weakness in the wrist and hand muscles may occur due to the altered biomechanics and instability associated with SLAC wrist. This weakness can affect your grip strength.
Clicking or Popping Sensation
Some individuals with SLAC wrist report a clicking or popping sensation in the wrist joint during movement. This can be due to the abnormal alignment of the wrist bones.
Instability
SLAC wrist results in instability of the wrist joint. You may feel that your wrist is giving way or that it is not as reliable in supporting activities that require wrist strength and stability.
Deformity
In the advanced stages of SLAC wrist, there may be visible deformities in the wrist joint.
It's important to note that SLAC wrist arthritis can be a progressive condition. Intervention, such as splinting, physical therapy, or SLAC wrist surgery, may be necessary to manage and alleviate the symptoms. If you suspect you have SLAC wrist or are experiencing any of these symptoms, it's advisable to consult a hand and wrist specialist, for a proper evaluation and treatment plan.
SLAC Wrist Treatment
Treatment options for SLAC wrist arthritis are aimed at reducing pain. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and individual patient factors.
Let’s take a closer look at how SLAC wrist treatment may alleviate pain, improve wrist function, and prevent further joint deterioration.
Splinting and Immobilization
In the early stages of SLAC wrist, wearing a splint or brace may help stabilize the joint and relieve pain. Immobilization can allow the injured ligaments or structures to heal.
Pain Management with Medication or Topical Treatments
Pain management with medications is an essential component of the treatment plan for SLAC wrist to help alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve the patient's overall comfort. The choice of medications and their use may vary depending on the severity of pain and individual patient needs.
Here are some common medications used for pain management in SLAC wrist treatment:
Over-the-counter (OTC) Pain Relievers
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve), can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with SLAC wrist. They are readily available without a prescription but should be used as directed and with caution, as long-term use can have side effects like stomach irritation or GI bleeds.
Prescription NSAIDs
If over-the-counter NSAIDs are not providing sufficient pain relief, your healthcare provider may prescribe stronger NSAID medications.
Oral Steroids
In some cases, short-term use of oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. These are typically used in acute situations.
Topical NSAIDs
Creams or gels containing NSAIDs, such as diclofenac gel, can be applied directly to the wrist joint to reduce localized pain and inflammation.
Hot and Cold Therapy
Hot and cold therapy can be helpful in managing the symptoms of SLAC wrist but their effectiveness depends on the specific symptoms and stages of the condition.
Heat Therapy for SLAC Wrist
Heat therapy can be useful in SLAC wrist primarily for relieving pain, reducing muscle tension, and improving joint flexibility.
Use heat for SLAC wrist:
- When experiencing chronic pain or stiffness associated with SLAC wrist.
- Before performing gentle wrist stretches or exercises as part of physical therapy to enhance muscle and joint flexibility.
- To relax the wrist muscles before engaging in activities that require wrist mobility.
Ice Therapy for SLAC Wrist
Ice therapy, on the other hand, is typically more relevant during the acute phases of SLAC wrist or when inflammation is a significant issue. It helps reduce swelling, numb the area, and alleviate pain.
Use ice for SLAC wrist:
- After a recent injury or flare-up of SLAC wrist to control swelling and reduce pain.
- If you notice increased inflammation or swelling in the wrist joint.
- Following activities that may exacerbate symptoms, such as heavy lifting or repetitive wrist motions.
Corticosteroid Injections
In some cases of SLAC wrist, corticosteroid injections into the wrist joint may provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation. However, these injections are typically used cautiously due to concerns about potential joint damage with repeated use.
SLAC Wrist Surgery Options
If the pain from SLAC wrist is not well controlled and the patient cannot tolerate the symptoms, surgery may be recommended as a SLAC wrist treatment option. There are several surgical options available, each with its own set of risks and benefits. The type of surgery recommended is often based on the pattern of arthritis seen on the patient’s X-rays and other specific patient factors.
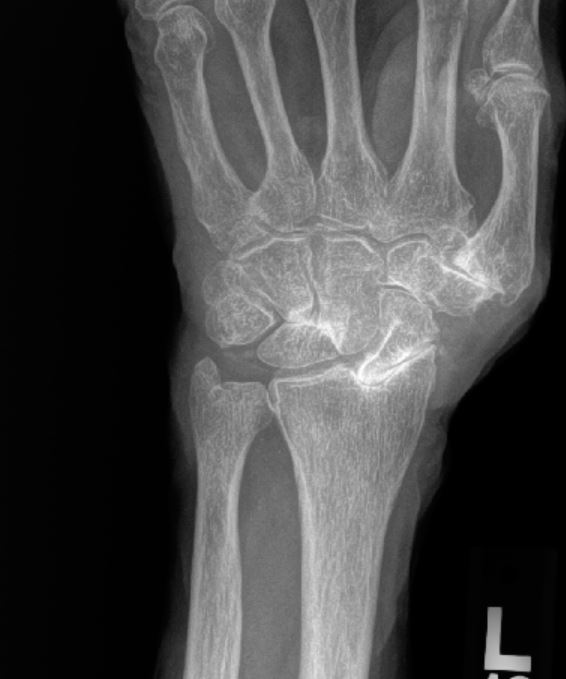
Let’s explore the potential SLAC wrist surgery options that may benefit patients suffering from arthritis of the wrist.
Partial Wrist Denervation
This SLAC wrist surgery option is designed to reduce wrist pain by removing nerves in the wrist that supply pain signals to the brain. Only selected nerves that transmit pain are cut. The nerves which provide feeling to the fingers and the nerves which control muscle movement of the hand are protected. This procedure has a quick recovery and low complication rate, but it may not fully relieve pain in some patients.
Partial wrist denervation can be considered as an option for pain management in cases where SLAC wrist has resulted in significant chronic pain that is not adequately controlled with other treatments. Surgeons may combine PWD with other surgical interventions, such as wrist fusion or wrist joint replacement, depending on the patient's specific needs.
Proximal Row Carpectomy (PRC)
This SLAC wrist surgery, also known as “three bone excision,” is designed to reduce pain by removing the arthritic bones in the wrist, specifically the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum bones. Occasionally the tip of the radius bone is also removed if needed. This proximal row carpectomy surgery allows the remaining non-arthritic bones to serve as the new wrist joint.
It can take up to 6 weeks to heal following this procedure, and not every patient gets full pain relief. About 50% of wrist motion can be maintained afterward. In some patients, the effects of PRC surgery can wear out and require a total wrist fusion in the future.
Partial Wrist Fusion
A partial wrist fusion surgery reduces pain by fusing together specific arthritic bones in the wrist. Often the scaphoid bone is removed during this surgery as well. Screws, staples, or a plate are options used to fix the bones, which require several weeks to heal in a cast. Smokers are at higher risk of healing complications with this procedure. About 50% of wrist motion can be maintained. In some patients, this SLAC wrist surgery can wear out and require a total wrist fusion in the future.
Total Wrist Fusion (Wrist Arthrodesis)
A total wrist fusion is the most effective SLAC wrist surgery when it comes to reducing wrist pain, but all wrist motion is eliminated. Because the major wrist bones are fused together, the wrist is no longer capable of flexion and extension movement. A plate and screws are typically used to fix the bones. As in other fusion surgeries, smokers are at higher risk of healing problems. Revision surgery in the future is not common after this procedure.
Wrist Joint Replacement (Total Wrist Arthroplasty)
Wrist joint replacement involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial implant to improve pain and function. It is performed to address both structural issues and pain. This surgery replaces the arthritic joint with an artificial implant, similar to a knee replacement. This surgery is the least common option in our practice, as there are very few patients who are good candidates for this option. There is a high complication rate, such as implant loosening, breakage, infection, and revision surgery, making it a less desirable option for SLAC wrist treatment.
Ultimately, the choice of which SLAC wrist surgery option is the right one for you depends on the individual patient's condition, the underlying causes of pain, and the goals of treatment. It is important for patients to discuss their options with a qualified hand and wrist surgeon from Raleigh Hand to Shoulder Center in order to determine the most appropriate surgical approach for their particular case of SLAC wrist.
Find Relief from SLAC Wrist Arthritis
SLAC wrist arthritis can be very painful, but our expert team at Raleigh Hand to Shoulder Center is here to help you find relief and restore wrist function. Call our office to make an appointment or book a visit online!

Updated 6/22/2025

